Discover Diaphragmatic Breathing: Reduce Anxiety in 5 Minutes

Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, is a powerful technique that can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms by promoting relaxation and improving oxygen flow in just a few minutes.
Feeling overwhelmed by anxiety? Discover the Power of Diaphragmatic Breathing: Reduce Anxiety Symptoms by 25% in Just 5 Minutes with this simple, yet effective technique that can be practiced anywhere, anytime, offering immediate relief.
Understanding Diaphragmatic Breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, is a type of breathing exercise that engages the diaphragm, a large muscle located at the base of the lungs. Unlike shallow chest breathing, diaphragmatic breathing promotes deeper, fuller breaths, leading to a host of physiological and psychological benefits.
By consciously shifting the focus from the chest to the abdomen, individuals can enhance their body’s natural relaxation response, effectively counteracting the physical symptoms of anxiety and stress.
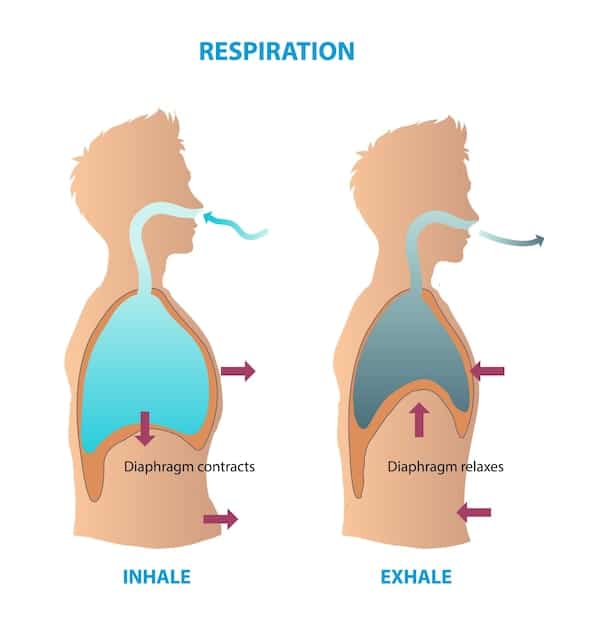
The Science Behind the Breath
When we experience anxiety, our bodies often enter a state of “fight or flight,” driven by the sympathetic nervous system. This can lead to rapid, shallow breathing, increased heart rate, and muscle tension. Diaphragmatic breathing, on the other hand, activates the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” response.
This activation helps to slow the heart rate, lower blood pressure, and relax muscles, effectively reducing the physical manifestations of anxiety.
Benefits Beyond Anxiety Reduction
While reducing anxiety symptoms is a significant benefit, diaphragmatic breathing offers a range of other advantages, including improved sleep quality, increased energy levels, and better emotional regulation. Regular practice can also lead to enhanced focus and concentration, contributing to overall well-being.
- Improved oxygen intake, nourishing cells and tissues throughout the body.
- Reduced strain on neck and shoulder muscles, alleviating tension headaches.
- Enhanced core stability, contributing to better posture and balance.
- Increased awareness of bodily sensations, fostering mindfulness and self-compassion.
In summary, understanding the mechanics and benefits of diaphragmatic breathing provides a solid foundation for incorporating this technique into daily life, offering a readily available tool for managing anxiety and promoting overall wellness.
Step-by-Step Guide to Diaphragmatic Breathing
Mastering diaphragmatic breathing takes a little practice, but the steps are simple and can be easily integrated into your daily routine. Find a quiet space where you can relax without distractions. Whether you choose to sit, lie down, or stand, ensure your body is in a comfortable position.
Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you effectively practice diaphragmatic breathing:
Getting Started
Begin by either lying on your back with your knees bent or sitting comfortably in a chair. Place one hand on your chest and the other on your abdomen, just below your rib cage. This positioning will help you monitor your breathing and ensure you’re engaging your diaphragm correctly.
Close your eyes gently, further reducing distractions and allowing you to focus on your breath.
The Breathing Technique
Inhale slowly and deeply through your nose, allowing your abdomen to rise as your diaphragm moves downward. The hand on your chest should remain relatively still, while the hand on your abdomen rises noticeably. This indicates that you are breathing from your diaphragm.
- Inhale deeply, counting to four as air fills your lungs.
- Hold your breath for a count of one.
- Exhale slowly and completely through your mouth, pursing your lips as if you’re gently blowing out a candle.
- Repeat this cycle for 5-10 minutes, focusing on each breath and the movement of your abdomen.
Remember to breathe deeply and gently throughout the exercise. Aim to make sure that your abdomen is expanding, and your chest is relatively still.
Troubleshooting Tips
If you find it difficult to engage your diaphragm, try practicing in front of a mirror to observe your chest and abdomen. You can also place a book on your abdomen to provide a visual cue and encourage the correct movement.
Be patient with yourself, as it may take some time to master the technique. With consistent practice, diaphragmatic breathing will become more natural and effortless.
By following these steps, you can effectively practice diaphragmatic breathing, tapping into its powerful potential to reduce anxiety and promote relaxation.
Integrating Diaphragmatic Breathing into Your Daily Life
Once you’ve mastered the basic technique, integrating diaphragmatic breathing into your daily life can provide ongoing benefits throughout the day. There are various opportunities to incorporate this practice into your routine, enhancing its effectiveness and making it a natural part of your stress management toolkit. Consider specific scenarios or events that typically trigger feelings of anxiety or stress.
Then, plan to implement diaphragmatic breathing just before, during, or after these times to proactively manage your response.

Practical Application in Different Scenarios
Before a stressful meeting or presentation, take a few minutes to practice diaphragmatic breathing to calm your nerves and improve your focus. During a traffic jam or commute, use this technique to ease frustration and reduce tension. Before bedtime, incorporate diaphragmatic breathing into your relaxation routine to promote restful sleep.
Here are some specific examples of when and how to use diaphragmatic breathing:
- Morning Routine: Start your day with 5-10 minutes of diaphragmatic breathing to set a calm and focused tone.
- Work Breaks: Take short breaks throughout the day to practice diaphragmatic breathing, helping to reduce stress and improve concentration.
- Before Sleep: Incorporate diaphragmatic breathing into your bedtime routine to promote relaxation and improve sleep quality.
Consider these as ideas on ways that you can easily make this part of your everyday activities. The repetition is key to helping it become a habit over time, so you can reduce stress throughout your day.
Mindfulness and Consistency
Combining diaphragmatic breathing with mindfulness practices can amplify its effects. Pay attention to the sensations in your body as you breathe, noticing the rise and fall of your abdomen and the flow of air in and out of your lungs. This mindfulness helps to anchor you in the present moment, reducing rumination and worry.
Consistency is key to experiencing the full benefits of diaphragmatic breathing. Aim to practice regularly, even when you’re not feeling particularly anxious or stressed. This will help to build a strong foundation for managing anxiety in the long term.
By integrating diaphragmatic breathing into your daily life and combining it with mindfulness practices, you can create a powerful and sustainable approach to managing anxiety and promoting overall well-being.
Tracking Your Progress and Measuring Results
Monitoring your progress as you incorporate diaphragmatic breathing into your routine can be both motivating and insightful. By tracking your experiences, you can gain a deeper understanding of how this technique impacts your anxiety levels and overall well-being. Keeping a journal will help you log your progress and provide insights.
Creating a simple tracking template can help you identify patterns and trends that inform your practice.
Creating a Tracking Template
Design a simple template that includes key metrics such as frequency of practice, duration, and subjective ratings of anxiety levels. This template can be a physical journal, a spreadsheet, or a note-taking app on your smartphone.
Include space for notes, allowing you to capture specific details about your experiences, such as the time of day, the environment, and any accompanying thoughts or emotions.
Analyzing the Data
Review your tracking data regularly to identify patterns and trends. Are there certain times of day when diaphragmatic breathing is most effective? Are there specific situations that trigger a greater reduction in anxiety symptoms? Understanding these patterns can help you tailor your practice to maximize its benefits.
- Anxiety Levels: Rate your anxiety levels before and after each session on a scale of 1 to 10.
- Sleep Quality: Track your sleep quality by noting how easily you fall asleep and how rested you feel in the morning.
- Overall Well-being: Assess your overall sense of well-being on a regular basis, noting any improvements in mood, energy levels, or focus.
The more consistent you are with tracking, the better you will get at identifying patterns and trends that you can use to your advantage, particularly for times you know that you will need it.
Seeking Professional Guidance
While tracking your progress can provide valuable insights, it’s also important to seek professional guidance from a healthcare provider or therapist. They can offer additional support and expertise, helping you to optimize your diaphragmatic breathing practice and address any underlying anxiety issues.
They may also suggest other techniques or therapies that can complement diaphragmatic breathing, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) or mindfulness meditation.
By tracking your progress, analyzing the data, and seeking professional guidance, you can gain a deeper understanding of the impact of diaphragmatic breathing on your anxiety levels and overall well-being, empowering you to take control of your mental and emotional health.
Addressing Common Challenges and Misconceptions
While diaphragmatic breathing is a simple technique, individuals may encounter challenges or misconceptions that hinder their progress. Addressing these issues proactively can help to ensure a more positive and effective experience. You may find it difficult to adjust to this type of breathing if you tend to breathe more from your chest.
Understanding these common challenges can provide the solution you need to ensure its success.
Common Challenges
One common challenge is difficulty engaging the diaphragm, leading to shallow chest breathing instead of deep abdominal breathing. Some individuals may also experience feelings of lightheadedness or dizziness when they first start practicing diaphragmatic breathing.
Others may struggle to maintain consistency or find it difficult to integrate the technique into their daily routine. These are all normal challenges that can be overcome with patience and practice.
Misconceptions about Diaphragmatic Breathing
One misconception is that diaphragmatic breathing is only effective for managing anxiety in the moment. While it can provide immediate relief, regular practice can also lead to long-term improvements in anxiety levels and overall well-being.
- It’s a Quick Fix: Diaphragmatic breathing is a valuable tool for managing anxiety, it’s not a substitute for professional treatment.
- It’s Complicated: Diaphragmatic breathing is a simple and natural technique that can be easily learned and practiced by anyone.
- It’s a Cure-All: Diaphragmatic breathing as part of a comprehensive approach to managing anxiety and promoting overall well-being is most effective.
Understanding what the goal really is by doing this type of breathing can help you keep it as a tool in your toolbelt. Using it when you remember will add up over time to become a great habit.
Overcoming Challenges and Dispelling Misconceptions
To overcome challenges, focus on engaging your diaphragm consciously, using visual cues such as placing a hand on your abdomen or practicing in front of a mirror. If you experience lightheadedness, slow down your breathing and take breaks as needed.
To dispel misconceptions, educate yourself about the benefits and limitations of diaphragmatic breathing, and seek guidance from a healthcare provider or therapist.
By addressing common challenges and dispelling misconceptions, you can create a more positive and effective diaphragmatic breathing practice, maximizing its benefits for anxiety management and overall well-being. Remember, practice makes perfect.
The Long-Term Impact of Consistent Practice
The true power of diaphragmatic breathing lies not just in its immediate effects, but in the long-term impact of consistent practice. Regular engagement with this technique can lead to profound and lasting changes in your mental, emotional, and physical well-being. Make sure that you are finding a time that works for you so it has the best chance of becoming a habit.
Once you have mastered it, you can take it with you to use anytime, so make it a priority.
Enhanced Stress Resilience
Consistent diaphragmatic breathing helps to build resilience to stress, making you better equipped to handle challenges and setbacks. By regularly activating the parasympathetic nervous system, you strengthen your body’s natural relaxation response, reducing the impact of stress hormones and promoting a sense of calm and well-being.
This enhanced stress resilience can translate into improved performance at work, stronger relationships, and greater overall life satisfaction.
Improved Emotional Regulation
Diaphragmatic breathing can also improve emotional regulation, helping you to manage difficult emotions more effectively. As you become more aware of your breath and body sensations, you develop greater self-awareness and emotional intelligence.
- Reduced reactivity to stressors, preventing escalation into full-blown anxiety attacks.
- Improved emotional regulation, allowing for more balanced and adaptive responses to challenges.
- Increased self-awareness, fostering mindfulness and compassion towards oneself and others.
By getting good at diaphragmatic breathing and its benefits, you can expect great benefits in many other aspects of your life as well.
Sustained Physical Benefits
In addition to mental and emotional benefits, consistent diaphragmatic breathing can also lead to sustained physical improvements. These include lower blood pressure, reduced muscle tension, improved sleep quality, and increased energy levels.
These physical benefits can contribute to a greater sense of vitality and well-being, making you feel more energized, focused, and capable of tackling life’s challenges.
By embracing diaphragmatic breathing as a long-term practice, you can unlock its full potential for transforming your life, fostering resilience, improving emotional regulation, and promoting sustained physical well-being. The time commitment needed for it is minimal compared to the benefits you will get.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 🧘 Proper Technique | Inhale deeply through your nose, feeling your abdomen rise. Exhale slowly through your mouth. |
| ⏱️ Consistent Practice | Set aside 5-10 minutes daily, even when not stressed, to make it a habit. |
| 📈 Tracking Results | Monitor anxiety levels, sleep quality, and overall well-being to measure progress. |
| 💪 Long-Term Benefits | Improved stress resilience, better emotional regulation, and sustained physical well-being. |
What exactly is diaphragmatic breathing?
▼
Diaphragmatic breathing, also known as belly breathing, involves engaging the diaphragm muscle to promote deeper, fuller breaths. This type of breathing helps to maximize oxygen intake and activate the body’s relaxation response, reducing anxiety and stress.
▼
Diaphragmatic breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for the “rest and digest” response. This helps to slow the heart rate, lower blood pressure, and relax muscles, effectively reducing the physical symptoms of anxiety.
▼
You can practice diaphragmatic breathing at any time, but it’s particularly helpful during moments of stress or anxiety. Incorporating it into your morning routine, work breaks, or before bedtime can also provide ongoing benefits.
▼
Common challenges include difficulty engaging the diaphragm, shallow chest breathing, and lightheadedness. Practice, patience, and seeking guidance from a healthcare provider can help overcome these challenges.
▼
While diaphragmatic breathing is a valuable tool for managing anxiety, it’s not a substitute for professional treatment. It’s most effective when used as part of a comprehensive approach that may include therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Incorporating diaphragmatic breathing into your daily routine is a simple yet powerful tool for managing anxiety and improving overall well-being. By understanding the technique, integrating it into your life, tracking your progress, and addressing common challenges, you can unlock its full potential and experience lasting positive changes.





